Power Throttling Perfection: Optimizing Battery Life in Windows 10
Introduction
In the era of mobile computing and on-the-go productivity, battery life is a precious commodity. Recognizing the significance of efficient power consumption, Microsoft introduced Power Throttling in Windows 10, a feature designed to optimize battery life without compromising performance. This comprehensive guide, titled “Power Throttling Perfection: Optimizing Battery Life in Windows 10,” delves into the intricacies of Power Throttling, unveiling its features, benefits, and the science behind energy-efficient computing. From understanding CPU power states to configuring Power Throttling settings, this guide aims to empower users with the knowledge needed to unlock the full potential of their device’s battery life.
Understanding Power Throttling: Balancing Performance and Efficiency
Power Throttling is a power management feature in Windows 10 that dynamically adjusts the power consumption of background processes, ensuring that they run in an energy-efficient manner. By intelligently throttling the CPU power states of background applications, Power Throttling minimizes power usage without sacrificing the performance of foreground tasks. This balance between performance and efficiency is particularly crucial for portable devices, such as laptops and tablets, where optimizing battery life is a top priority.
Key Features of Power Throttling:
- Dynamic Power Management: Power Throttling operates dynamically, analyzing the activity of background processes and adjusting their CPU power states accordingly. This ensures that energy-intensive tasks are limited when they are running in the background, conserving power for foreground applications.
- Foreground and Background Differentiation: Power Throttling distinguishes between foreground and background processes, prioritizing power allocation for tasks actively in use. Foreground applications, those currently visible to the user, receive higher CPU power states to maintain optimal performance.
- Energy-Efficient Background Processing: Background processes are intelligently managed to run in lower CPU power states, reducing power consumption while still allowing them to perform necessary tasks. This results in a more energy-efficient operation for background applications, contributing to extended battery life.
- User Customization: Windows 10 users have the ability to customize Power Throttling settings based on their preferences. This includes adjusting the aggressiveness of power management and specifying which apps are exempt from Power Throttling.
The Science Behind Power Throttling: CPU Power States Unveiled
To understand the science behind Power Throttling, it’s essential to explore the concept of CPU power states. A CPU (Central Processing Unit) can operate in various power states, each representing a different level of power consumption and performance. The key CPU power states are:
- C0 (Active State): The CPU is fully active and executing instructions. This state corresponds to the highest level of power consumption.
- C1 (Halt State): The CPU is idle, and the clock signal is halted. Power consumption is reduced compared to the active state.
- C2, C3 (Deeper Sleep States): Successive deeper sleep states represent further reductions in power consumption. In these states, additional components of the CPU, such as cache memory, may be powered down to save energy.
Power Throttling leverages these CPU power states to manage the power consumption of background processes effectively. By transitioning background applications to lower power states, Power Throttling achieves energy efficiency without compromising the responsiveness of foreground tasks.
Activating Power Throttling: Customizing Energy Efficiency
Power Throttling is an integral part of Windows 10, and it is automatically active on supported devices. However, users have the flexibility to customize Power Throttling settings based on their preferences. Here’s a step-by-step guide to accessing and configuring Power Throttling settings:
- Access Power Options: Open the “Settings” app on the Windows 10 device by clicking on the Start menu and selecting the gear icon (or by pressing
Win + I). Navigate to “System” and then click on “Power & sleep.” - Access Additional Power Settings: In the Power & sleep settings, scroll down and click on the “Additional power settings” link. This will open the Power Options control panel.
- Choose a Power Plan: Within the Power Options control panel, select the power plan you wish to customize. The recommended plan for most users is the “Balanced” power plan, as it offers a good balance between performance and energy efficiency.
- Configure Power Throttling Settings: Click on “Change plan settings” next to the selected power plan, then click on “Change advanced power settings.” In the Advanced settings window, locate the “Processor power management” category. Here, you will find the “System cooling policy” and “Processor performance core parking min cores” settings, which are related to Power Throttling.
- Adjust Power Throttling Settings: Under “Processor power management,” you can adjust the “System cooling policy” to control how the system manages cooling and performance. Additionally, you can modify the “Processor performance core parking min cores” setting to configure the minimum number of processor cores that should be parked during periods of low activity.
- Save Changes: Once you’ve adjusted the Power Throttling settings according to your preferences, click “Apply” and then “OK” to save the changes.
Benefits of Power Throttling: Maximizing Battery Life
Power Throttling in Windows 10 offers a multitude of benefits, all geared towards maximizing battery life and enhancing the energy efficiency of devices.
- Extended Battery Life: The primary benefit of Power Throttling is the extension of battery life for portable devices. By intelligently managing the power consumption of background processes, Power Throttling ensures that energy is allocated efficiently, resulting in longer battery life.
- Balanced Performance: Power Throttling strikes a balance between performance and efficiency. While background processes are managed to be energy-efficient, foreground tasks continue to receive the necessary CPU power states to maintain optimal performance. This ensures that users enjoy a responsive computing experience.
- Customizable Settings: Windows 10 users have the ability to customize Power Throttling settings based on their preferences. Whether adjusting the aggressiveness of power management or specifying exempted apps, customization options empower users to tailor the feature to their unique usage patterns.
- Background Process Efficiency: Power Throttling enhances the efficiency of background processes by allowing them to operate in lower CPU power states. This results in energy savings without compromising the functionality of background applications.
- Automatic and Seamless Operation: Power Throttling operates automatically in the background, requiring minimal user intervention. The seamless transition between CPU power states ensures that users experience the benefits of energy efficiency without disruptions to their workflow.
- Device Cooling and Noise Reduction: By managing the cooling policy, Power Throttling contributes to reduced heat generation in the device. This not only enhances energy efficiency but also leads to less frequent fan activation, contributing to a quieter computing experience.
Power Throttling Best Practices: Ensuring Optimal Efficiency
While Power Throttling operates automatically and is designed to enhance efficiency, users can adopt certain best practices to ensure optimal performance and energy savings:
- Regularly Update Windows: Keeping Windows 10 up to date ensures that the latest enhancements and optimizations, including those related to Power Throttling, are applied to the operating system.
- Optimize Background Apps: Review and optimize the list of background apps running on the device. Reducing the number of unnecessary background processes can further contribute to energy savings.
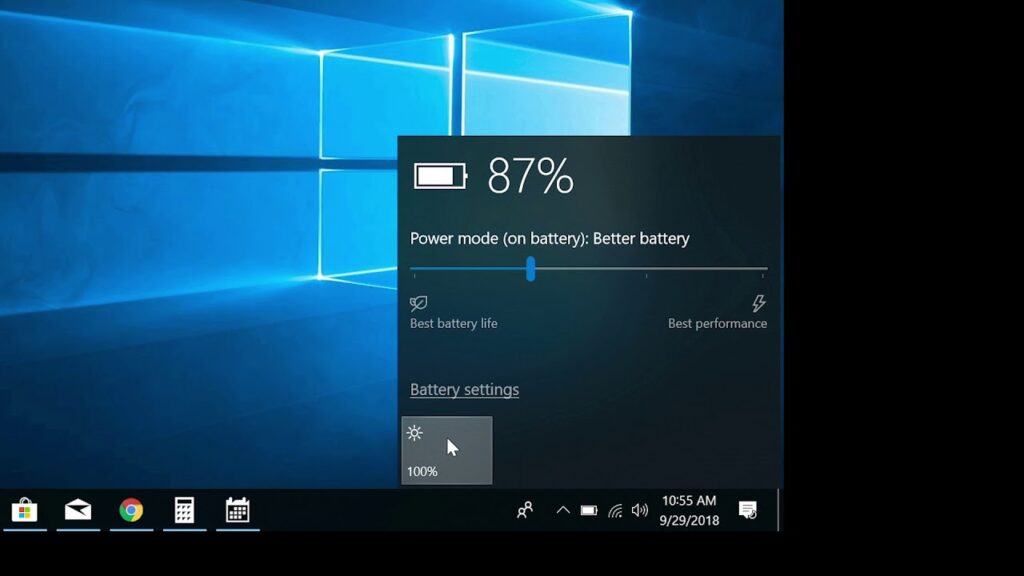
- Utilize Battery Saver Mode: On laptops and tablets, utilizing the Battery Saver mode can complement Power Throttling efforts. Battery Saver mode conserves energy by adjusting system settings and background activity.
- Monitor Power Consumption: Utilize built-in tools or third-party applications to monitor power consumption and identify any power-hungry processes. This awareness allows users to take corrective actions, such as closing resource-intensive apps.
- Adjust Power Plans: Depending on the usage scenario, users can switch between power plans to optimize settings for specific tasks. For example, switching to the “Power Saver” plan when performing less demanding activities can maximize energy savings.
Conclusion
Power Throttling in Windows 10 represents a significant stride towards achieving the delicate balance between performance and energy efficiency. By intelligently managing CPU power states for background processes, Power Throttling ensures that devices deliver a responsive experience while maximizing battery life.
As the digital landscape continues to evolve, where mobility and productivity go hand in hand, features like Power Throttling become instrumental in shaping a user-friendly and energy-efficient computing experience. Power Throttling is not just a feature; it’s a commitment to optimizing the core of device performance, ensuring that users can enjoy extended battery life without compromising the capabilities of their Windows 10 devices.
By understanding the science behind Power Throttling, customizing settings to align with individual preferences, and adopting best practices for energy efficiency, users can unlock the full potential of their device’s battery life. Power Throttling perfection is not just a goal; it’s a journey towards a future where computing is both powerful and sustainable, contributing to a more efficient and eco-conscious digital experience.