Navigating the Tech Terrain: A Comprehensive Guide to Finding Your GPU Model on Windows 10
Introduction
Understanding the hardware components of your Windows 10 computer is essential for various reasons, from troubleshooting performance issues to ensuring compatibility with software and games. One crucial piece of hardware is the Graphics Processing Unit (GPU), responsible for rendering graphics and enhancing overall visual experiences. This comprehensive guide is designed to walk you through the steps of finding your GPU model on Windows 10, catering to users with varying levels of technical expertise.
Section 1: Overview of the GPU
1.1 What is a GPU?
The Graphics Processing Unit, commonly known as the GPU, is a specialized electronic circuit responsible for rendering images and videos on your computer’s display. It handles complex calculations related to graphics, ensuring smooth visuals in applications, games, and multimedia content.
1.2 Importance of Knowing Your GPU Model
Understanding your GPU model is crucial for several reasons:
- Performance Monitoring: Knowing your GPU model helps monitor its performance and identify potential issues.
- Driver Updates: Properly identifying your GPU allows you to download and install the correct graphics drivers, ensuring optimal functionality.
- Software Compatibility: Some software and games may have specific requirements or optimizations based on the GPU model, making it essential to know your hardware for compatibility.
Section 2: Identifying Your GPU Model
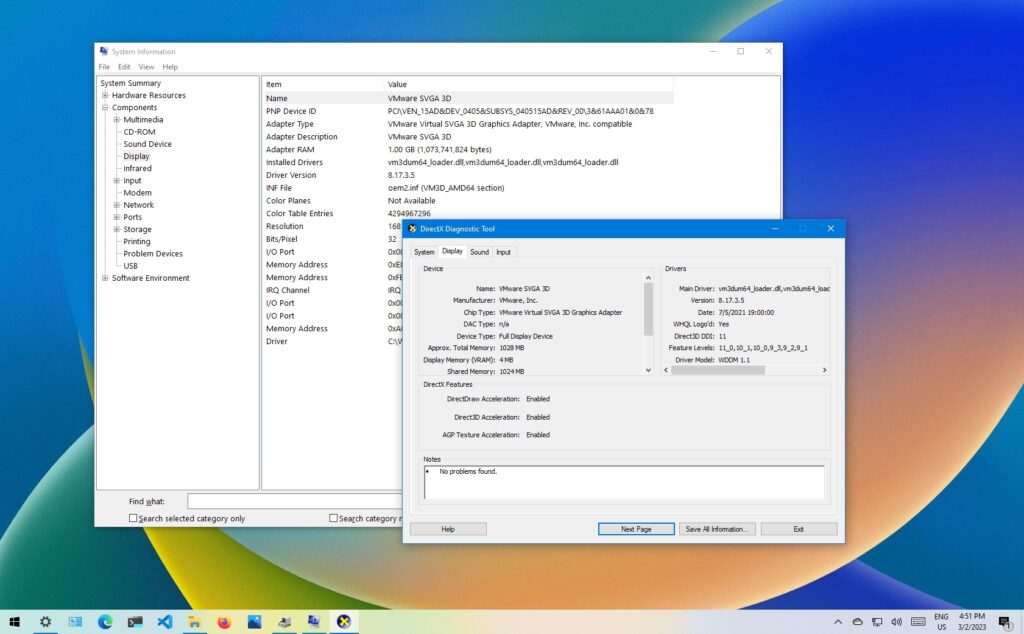
2.1 Using System Information
The System Information tool in Windows 10 provides detailed information about your computer’s hardware components, including the GPU.
- Press the
Windows key + Rto open the Run dialog. - Type “msinfo32” and press Enter.
- In the System Information window, expand “Components” in the left pane and select “Display.”
The right pane will display information about your GPU, including the manufacturer and model.
2.2 Device Manager Method
The Device Manager is another built-in tool that allows you to view and manage hardware devices, including the GPU.
- Right-click on the Start button and select “Device Manager.”
- Expand the “Display adapters” category to reveal your GPU model.
Note: The name listed here may not always match the marketing name of your GPU, but it provides a starting point for further investigation.
2.3 DirectX Diagnostic Tool
The DirectX Diagnostic Tool provides detailed information about DirectX components, including your GPU.
- Press the
Windows key + Rto open the Run dialog. - Type “dxdiag” and press Enter.
- In the DirectX Diagnostic Tool window, navigate to the “Display” tab.
The “Name” field will typically display your GPU model.
Section 3: GPU-Z Software
3.1 Introduction to GPU-Z
GPU-Z is a third-party software tool designed specifically for retrieving detailed information about your GPU. It provides comprehensive details, including the GPU model, core clock, memory clock, and more.
3.2 Download and Installation
- Visit the official GPU-Z website (https://www.techpowerup.com/gpuz/) to download the latest version.
- Install the software following the on-screen instructions.
3.3 Using GPU-Z
- Launch GPU-Z after installation.
- The main screen displays various details about your GPU, including the Name, GPU, and BIOS version.
GPU-Z is a powerful tool for enthusiasts and users who require in-depth information about their GPU’s specifications and capabilities.
Section 4: Command Line Method
4.1 Command Prompt
For users comfortable with the command line, Windows Command Prompt can provide information about the GPU.
- Press the
Windows key + Xand select “Command Prompt” (Admin) or “PowerShell” (Admin). - Type the following command and press Enter:bash
wmic path win32_videocontroller get caption
The output will display the name of your GPU.
Section 5: Checking GPU Information in Settings
5.1 Display Settings
Windows 10 Settings also offers a way to view basic GPU information.
- Right-click on the desktop and select “Display settings.”
- Scroll down and click on “Advanced display settings.”
- Under “Refresh rate,” click on “Display adapter properties.”
The Adapter tab in the window that opens will display your GPU information.
Section 6: Using Third-Party System Information Tools
6.1 CPU-Z
While primarily designed for CPU information, CPU-Z also provides details about your GPU.
- Download and install CPU-Z from the official website (https://www.cpuid.com/softwares/cpu-z.html).
- Launch CPU-Z and navigate to the “Graphics” tab for information about your GPU.
Section 7: Additional Considerations
7.1 GPU Manufacturers
It’s important to note that GPU models come from various manufacturers, such as NVIDIA, AMD, and Intel. When identifying your GPU, consider both the manufacturer and the specific model.
7.2 Integrated vs. Dedicated GPUs
Laptops and some desktops may have both integrated and dedicated GPUs. Integrated GPUs are part of the CPU, while dedicated GPUs are separate components. Be aware of which GPU you are identifying, especially in laptops with switchable graphics.
Conclusion
Identifying your GPU model on Windows 10 is a fundamental step in optimizing your computer’s performance, ensuring software compatibility, and troubleshooting graphics-related issues. Whether you prefer built-in tools like System Information and Device Manager, third-party applications like GPU-Z, or the command line, this comprehensive guide has provided multiple methods catering to users of varying technical expertise. Armed with knowledge about your GPU, you can make informed decisions regarding driver updates, software compatibility, and overall system maintenance, contributing to a more efficient and enjoyable computing experience.