Mastering the Art of Audio Capture: A Comprehensive Guide to Recording Audio in Pro Tools
Introduction:
Recording audio is a foundational step in the music production process, serving as the cornerstone for capturing performances, creating tracks, and bringing musical ideas to life. In the realm of professional audio production, Avid Pro Tools stands as a premier choice for recording, offering a comprehensive set of tools and features for capturing pristine audio with precision and clarity. In this exhaustive guide, we’ll embark on a deep dive into the art of recording audio in Pro Tools, exploring every aspect of the process from setting up your session to optimizing your recording workflow for professional-grade results.
Understanding Audio Recording in Pro Tools:
Before diving into the specifics of recording audio, let’s take a moment to understand the fundamental concepts and components involved:
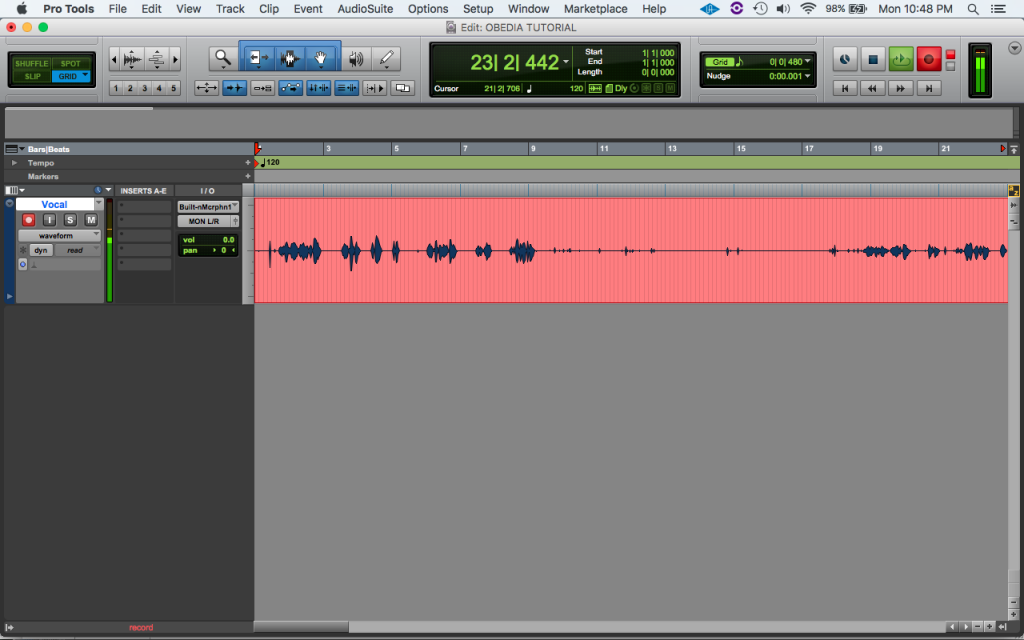
- Session Setup: A Pro Tools session serves as the container for your audio recordings, providing a workspace where you can organize tracks, record audio, and edit your recordings. Sessions can be created with specific settings such as sample rate, bit depth, and session format to ensure compatibility and consistency.
- Audio Tracks: In Pro Tools, audio recordings are typically captured on individual audio tracks, each representing a separate channel for recording and playback. Audio tracks can be created, named, and configured to suit your recording needs, such as mono or stereo recording, input selection, and monitoring options.
- Input Monitoring: Input monitoring allows you to monitor the audio signal coming into Pro Tools in real-time, enabling you to hear what you’re recording without latency or delay. Pro Tools offers various input monitoring modes, including Auto Input Monitoring, Input Only Monitoring, and Low Latency Monitoring, to accommodate different recording scenarios and preferences.
- Recording Modes: Pro Tools provides several recording modes to suit different recording scenarios and workflows. These include QuickPunch, Loop Recording, and Pre-roll/Post-roll recording, each offering unique features and capabilities for capturing audio with precision and flexibility.
Getting Started with Audio Recording:
Now that we have a basic understanding of audio recording in Pro Tools, let’s explore the step-by-step process of capturing audio in your session:
- Setting Up Your Session:
- Launch Pro Tools and create a new session or open an existing session where you want to record audio.
- Configure session settings such as sample rate, bit depth, and session format to match your recording requirements and preferences.
- Create audio tracks for recording by selecting Track > New from the menu bar and choosing the desired track type and configuration.
- Selecting Inputs and Outputs:
- Choose the input source for your audio recording by selecting the desired input from the input selector on the audio track. This could be an audio interface input, a microphone, or a virtual instrument.
- Configure output routing options to monitor your recording, ensuring that you can hear the audio signal coming into Pro Tools through your monitoring system or headphones.
- Setting Recording Levels:
- Adjust the input gain or preamp level on your audio interface to set the recording level for your microphone or input source. Aim to achieve a healthy signal level without clipping or distortion.
- Use the input meters in Pro Tools to monitor the incoming signal level and make adjustments as needed to optimize the recording level.
- Arming Tracks for Recording:
- Arm the audio track or tracks you want to record on by clicking the Record Enable button on each track. This prepares the tracks for recording and enables input monitoring for the selected inputs.
- Verify that the input monitoring mode is set to the desired setting (e.g., Auto Input Monitoring) to ensure that you can hear the audio signal during recording.
Advanced Recording Techniques:
Once you’re comfortable with the basics, consider exploring some advanced recording techniques to enhance your recording workflow and achieve professional-grade results:
- Multi-track Recording:
- Record multiple audio sources simultaneously by arming and recording on multiple audio tracks at once. This allows you to capture live performances, band rehearsals, or multi-microphone setups with ease.
- Use group and edit group functions in Pro Tools to manage and edit multiple tracks together, ensuring consistency and coherence in your recordings.
- Punch Recording:
- Use Punch Recording to fix or replace specific sections of a recording without re-recording the entire track. Set the punch-in and punch-out points in the timeline and engage Punch Recording mode to record only during the specified section.
- Experiment with QuickPunch mode for seamless punch-ins and punch-outs during playback, allowing for precise editing and correction of performances.
- Loop Recording:
- Use Loop Recording to capture multiple takes or iterations of a performance in succession. Set the loop range in the timeline and engage Loop Recording mode to record multiple passes automatically.
- Take advantage of playlist functionality in Pro Tools to organize and manage multiple takes or iterations of a recording, allowing for easy comparison and selection of the best performance.
Optimizing Your Recording Workflow:
As you become more comfortable with recording audio in Pro Tools, consider implementing some workflow optimizations to streamline your process and maximize efficiency:
- Customize Track Templates:
- Create custom track templates with predefined settings and configurations for different recording scenarios, such as vocal recording, drum tracking, or guitar recording. This allows you to save time and maintain consistency across multiple sessions.
- Use Track Presets:
- Save and recall track presets for commonly used settings and configurations, such as input routing, monitoring options, and plugin inserts. This enables you to quickly set up tracks for recording without having to manually configure each parameter.
- Keyboard Shortcuts and Macros:
- Learn and utilize keyboard shortcuts and macros to perform common recording tasks quickly and efficiently. Customize shortcuts for functions such as record, stop, play, and punch-in/out to streamline your recording workflow.
Conclusion:
Recording audio in Pro Tools is a fundamental aspect of the music production process, allowing you to capture performances, create tracks, and bring your musical ideas to life with precision and clarity. By mastering the art of audio recording in Pro Tools, you’ll be well-equipped to achieve professional-grade results and realize your creative vision in your productions.
Whether you’re recording vocals, instruments, or live performances, Pro Tools provides the tools, features, and flexibility you need to capture pristine audio with ease and confidence. So, dive in, experiment, and let the boundless possibilities of audio recording in Pro Tools inspire your musical journey.




