Unleashing Structural Integrity: A Comprehensive Guide to Weldments in SolidWorks
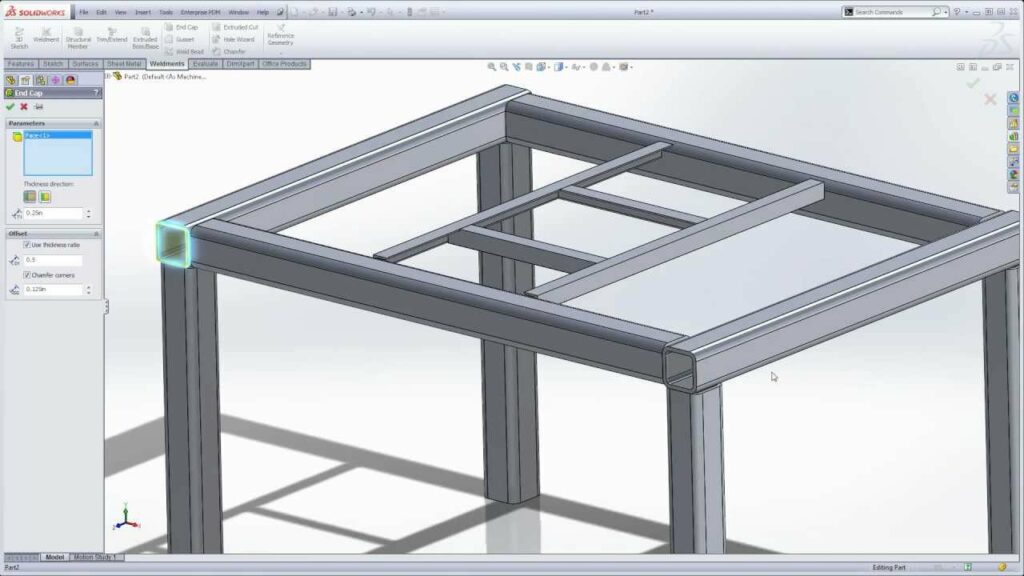
Weldments, a pivotal feature within SolidWorks, provide designers and engineers with a robust toolkit to construct welded structures and frames efficiently. In this extensive exploration, we delve deep into the realm of weldments in SolidWorks, elucidating their functionalities, advantages, and real-world applications across diverse engineering disciplines.
Understanding Weldments:
Weldments in SolidWorks facilitate the creation of welded structures by integrating various components, such as beams, tubes, and plates, through weld joints. These structures range from simple frames and trusses to complex assemblies, serving myriad purposes across industries such as construction, manufacturing, automotive, and aerospace.
At its essence, weldments enable designers to conceptualize, design, and fabricate welded structures seamlessly within the SolidWorks environment, leveraging an array of specialized tools and functionalities.
Key Concepts of Weldments in SolidWorks:
- Structural Members: Central to weldments are structural members, which encompass a wide range of predefined cross-sectional shapes such as I-beams, C-channels, tubes, angles, and custom profiles. These members serve as the building blocks for constructing welded structures, offering versatility and flexibility in design.
- Weld Beads: SolidWorks enables the creation of weld beads to simulate welding operations between structural members. Users can define weld bead properties such as size, type, and location, ensuring accurate representation of welded joints and connections within the assembly.
- End Treatments: Weldments support end treatments, which allow users to customize the end conditions of structural members for welding or fabrication purposes. End treatments include miter cuts, coping, notching, and trimming, enabling precise alignment and fit-up of members in welded assemblies.
- Cut Lists and Bills of Materials (BOMs): Weldments automatically generate cut lists and bills of materials (BOMs) based on the structural members and weldments included in the assembly. These lists provide detailed information on the quantity, length, size, and material of each component, streamlining the manufacturing and assembly process.
Benefits of Weldments in SolidWorks:
- Efficiency in Design: Weldments offer designers a streamlined workflow for creating welded structures, allowing for rapid prototyping and iteration. With a vast library of standard profiles and customizable features, designers can expedite the design process and explore multiple design concepts efficiently.
- Precision and Accuracy: SolidWorks ensures precision and accuracy in weldments through parametric modeling and intelligent features. Designers can define critical dimensions, tolerances, and geometric constraints, ensuring that welded structures meet exacting specifications and standards.
- Visualization and Analysis: Weldments provide powerful visualization and analysis tools to evaluate the integrity and performance of welded structures. Users can conduct structural simulations, finite element analysis (FEA), and motion studies to assess factors such as stress distribution, load-bearing capacity, and dynamic behavior.
- Integration with Manufacturing: SolidWorks seamlessly integrates weldments with manufacturing processes, enabling direct export of designs to computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) software or production machinery. This integration streamlines fabrication, reduces errors, and enhances efficiency in the manufacturing workflow.
Practical Applications of Weldments in SolidWorks:
- Frame and Chassis Design: Weldments are commonly used in the design of frames, chassis, and structural components for vehicles, machinery, and equipment. Designers leverage weldments to create robust and lightweight structures that withstand dynamic loads, vibrations, and environmental conditions.
- Support Structures: Weldments find applications in the construction of support structures such as trusses, frames, and platforms for architectural, industrial, and infrastructure projects. Designers use weldments to create stable and durable frameworks that provide structural support and stability in diverse environments.
- Material Handling Equipment: Weldments play a crucial role in the design of material handling equipment such as conveyors, racks, and shelving systems. Designers utilize weldments to fabricate sturdy and reliable structures that facilitate the storage, transport, and handling of materials in warehouses, factories, and distribution centers.
- Custom Fabrications: Weldments enable the creation of custom fabrications and specialty components for unique applications or bespoke projects. Designers leverage weldments to fabricate prototypes, one-off designs, and custom-built solutions that meet specific customer requirements and design criteria.
Conclusion:
Weldments in SolidWorks represent a versatile and indispensable tool for creating welded structures with precision, efficiency, and reliability. By leveraging structural members, weld beads, end treatments, and analysis tools, designers and engineers can conceptualize, design, and fabricate welded assemblies that meet stringent requirements and standards across diverse industries and applications. Whether used for frame and chassis design, support structures, material handling equipment, or custom fabrications, weldments remain a cornerstone of modern engineering workflows, enabling users to master complexity and achieve excellence in their designs.




