Mastering Tables: A Comprehensive Guide to Merging Cells in Microsoft Word
In the vast landscape of document formatting, tables serve as essential tools for organizing and presenting data in a structured and visually appealing manner. Whether you’re creating reports, resumes, or presentations, knowing how to manipulate tables effectively is key to achieving clear and concise document layouts. One fundamental operation in table formatting is merging cells, which allows you to combine multiple cells into a single larger cell. In this extensive guide, we’ll explore the intricacies of merging cells in Microsoft Word, empowering you to create professional and polished tables with ease and precision.
Understanding the Significance of Merging Cells:
Before delving into the practical aspects of merging cells, it’s crucial to grasp the significance of this operation in table design. Merging cells serves multiple purposes, including:
- Creating headers and labels: Merging cells enables users to create header rows or columns that span multiple columns or rows, providing clear labels and titles for data sets.
- Formatting complex layouts: Merging cells allows users to create complex table layouts, such as multicolumn headers, nested tables, or customized cell arrangements, to suit specific document formatting requirements.
- Enhancing visual clarity: Merging cells helps enhance the visual clarity and organization of tables by reducing clutter, minimizing empty space, and improving the overall aesthetic appeal of the table.
By incorporating merging cells into your table formatting toolkit, you can create tables that are not only functional and informative but also visually engaging and user-friendly.
Basic Merging Cells Functionality:
Merging cells in Microsoft Word is a straightforward process that can be accomplished using intuitive tools and commands. Here’s how to do it:
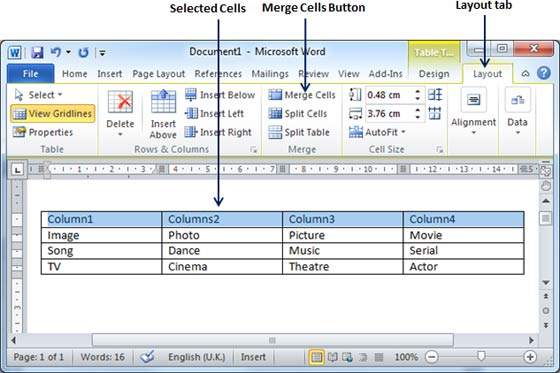
- Select Cells to Merge:
- Open Microsoft Word and navigate to the location in your document where the table is located.
- Click and drag to select the cells you want to merge. You can select cells in a single row, column, or across multiple rows and columns.
- Access the Merge Cells Command:
- With the cells selected, navigate to the “Layout” or “Table Design” tab located in the top menu bar.
- In the “Merge” group, you’ll find the “Merge Cells” button. Click on this button to merge the selected cells into a single larger cell.
- Verify Merged Cell:
- Once you’ve clicked the “Merge Cells” button, the selected cells will be merged into a single larger cell. The content of the upper-left cell will be retained, and the formatting of the merged cell will adjust accordingly.
Advanced Merging Cells Options:
While basic merging cells functionality suffices for most scenarios, Microsoft Word offers advanced features and customization options to further enhance table formatting and layout. Here are some additional features you may explore:
- Splitting Merged Cells:
- In cases where you need to reverse the merging operation, Word allows users to split merged cells back into individual cells. To split a merged cell, select the merged cell, then navigate to the “Layout” or “Table Design” tab and click on the “Split Cells” button.
- Merging Across Rows and Columns:
- Word enables users to merge cells across both rows and columns, creating custom cell configurations for specialized table layouts. Experiment with merging cells in different directions to achieve the desired table structure.
- Nested Tables:
- For more complex table layouts, Word supports the creation of nested tables within merged cells. This allows users to embed additional tables or content within a single cell, providing greater flexibility in table design.
Best Practices for Merging Cells Usage:
While merging cells offers versatility and functionality in table formatting, it’s essential to use it judiciously and in accordance with best practices. Here are some tips to consider:
- Maintain Consistency:
- When merging cells, strive to maintain consistency in cell sizes, alignments, and formatting throughout the table. Consistent formatting enhances visual clarity and readability.
- Use for Structural Elements:
- Reserve merging cells for structural elements such as headers, labels, or summary rows/columns that provide context and organization to the table content. Avoid overusing merging cells for decorative purposes or excessive formatting.
- Consider Accessibility:
- When designing tables with merged cells, consider accessibility guidelines to ensure that the table remains navigable and comprehensible for all users. Provide alternative text or descriptions for complex table structures to aid understanding.
- Test Across Devices:
- Before finalizing your table design, test the appearance and functionality of merged cells across different devices and display settings to ensure that the table renders correctly and maintains its integrity.
Conclusion:
Merging cells in Microsoft Word is a fundamental operation for creating clear, organized, and visually appealing tables. By mastering the basic merging cells functionality, exploring advanced options, and adhering to best practices for usage, you can create tables that effectively communicate information, enhance document readability, and convey professionalism. Whether you’re presenting data, organizing information, or designing layouts, merging cells offers a versatile and powerful tool for achieving your table formatting objectives with precision and efficiency. So, the next time you embark on a document creation journey in Word, remember to leverage the power of merging cells to create tables that captivate your audience and convey information with clarity and impact.




